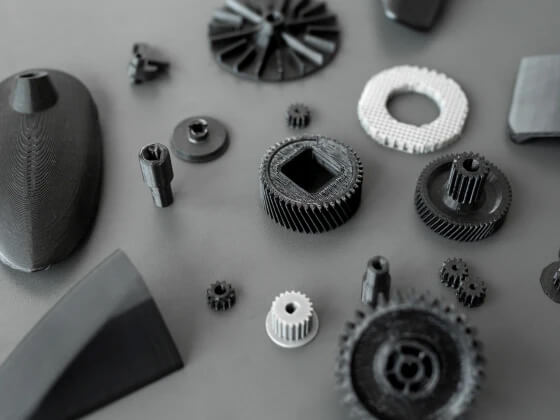
What Are Engineering Filaments?
Engineering filaments are specialized 3D printing materials known for their high strength, heat resistance, toughness, and chemical stability. They are perfect for creating prototypes, functional parts, jigs, and end-use components in demanding applications.
Why Choose Engineering Filaments?
Engineering filaments are purpose-built for industrial applications-robust enough to replace traditional methods like injection molding or CNC machining when printing functional, end-use parts.
Here's what makes them stand out:
Outstanding Mechanical Properties
High strength & Rigidity: Tensile strength of 50 -150 MPa, far above standard PLA (≈40 MPa), ideal for load-bearing parts.
High Toughness & Impact Resistance: 10-30% elongation at break and 60 KJ/m² impact strength, reducing risk of cracking under stress.
Heat Resistance: Withstands long-term use at 100°C-260°C, suitable for high-temp environments like car engine bays and aerospace components.
Chemical Resistance: Resistant to oils, acids, alkalis, and solvents,ideal for chemical seals and sterilizable medical parts.
High Wear Resistance & Low Friction: Materials like PA(nylon) and fiber-reinforced blends offer high surface hardness and low friction, perfect for gears, sliders and other wear-resistant parts.

Versatile Functional Features
Flame Retardant & Insulating: UL94 V-0 rated materials (e.g., modified PC) are great for electronic enclosures, preventing fire hazards.
Low Water Absorption & UV Resistance: ASA materials and weather-resistant PA maintain dimensional stability outdoors and resist UV damage.
Lightweight: Carbon fiber composites like PA-CF, PPS-CF combine the above features and make printed parts over 20% lighter than standard materials-top choice for drones designs.
High Transparency: PC materials offer over 90% light transmittance, suitable for optical lenses, light covers, and more.

Engineering Filaments Overview
| Material | Key Features | Typical Applications |
| PA(Nylon) |
|
Gears, bearings, moving mechanical parts, automotive seat adjusters, medical bone screw models |
| PC |
|
Optical lenses, electronics housings (e.g. router cases), tool handles, car lamp covers (heat and yellowing resistance). |
| PC-ABS |
|
Industrial equipment panels, consumer electronic housings (e.g., drone bodies), decorative parts in precision instruments. |
| PA(Nylon) |
|
Gears, bearings, moving mechanical parts, automotive seat adjusters, medical bone screw models |
| PEEK |
|
Aerospace structural parts (e.g. titanium substitutes), medical implants(e.g.spinal cages), corrosion-resistant semiconductor components. |
| PA6-CF | Carbon fiber-reinforced nylon with high strength, rigidity. impact resistance, and heat resistance. |
Automotive exhaust supports, kettle bases, pot handles engine brackets, gears, fuel pipe connectors, wear-resistant bearings |
| PA12-CF | Carbon fiber-reinforced PA12,featuring high strength. lightweight, low moisture absorption, heat resistance up to 175°C, and outstanding dimensional stability. | Fuel filter housings, pipe joints, robotic arms, ski bindings, climbing buckles, customized prosthetic joints, surgical tool handles |
| PA6-GF | Glass fiber-reinforced PA6 combining excellent mechanical performance with high strength, rigidity, and thermal resistance,excellent dimensional stability | Aerospace non-load-bearing components (e.g., brackets,connectors,dashboard parts), appliance housings, motor components, medical equipment shells, precision parts. |
Engineering Filament Guide:
Key Tips from Printing to Post-Processing
1. Drying before Printing
Materials like PA and Pc absorb moisture easily, Moisture >0.2% can cause bubbling during prints
Dry at80-110°c for 6-12 hours before printing.
Store in sealed containers with desiccant to keep dry.
2. Nozzle Selection
Fiber-reinforced filaments (e.g., PA+30% GF) are abrasive.
Brass nozzles can lead to wear and clogging.
Use hardened steel nozzles (hardness >HRC55 )to ensure durability
3. Optimal Printing Settings
.Nozzle Temp: PC: 280-320℃ | PEEK: 380-420℃ (Use an all-metal hotend)
·Bed Temp: PC: 80-100℃ I PA: 60-80℃
.Use glass or carbon fiber beds to boost adhesion
.Printing Environment:
.Enclosed chamber at 50-70℃ helps prevent warping, especially for PC/PEEK.
.Apply high-temp glue on edges
.Print at 30-50mm/s to reduce internal stress
4. Post-Processing - Annealing
Anneal finished prints at 10-20℃ above Tg (e.g., 110℃ for Pc) for 1-2 hours.
Then cool slowly to room temp
Benefits:
.Relieves internal stress
.Boosts part strength by 15-20%
.Reduces cracking over time
Unlock more possibilities with engineering filaments.
Follow @inslogic3D for tips, materials, and more!
Website: inslogic3d.com
Store: store.inslogic3d.com