1. Understanding 3D Printing Filament Types
Different filaments have unique properties, affecting strength, flexibility, durability, and printability. Here are the most common types:
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
✅ Pros:
-
Easy to print (great for beginners)
-
Biodegradable and eco-friendly
-
Low warping, no heated bed required
-
Strength & durability
- Better layer adhesion
❌ Cons:
-
Low heat resistance (can deform in hot environments)
-
Brittle compared to other filaments
Best for: Prototyping & design, Architecture models, Education & visualization, Everyday use, Art
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
✅ Pros:
-
Strong and flexible (good layer adhesion)
-
Good chemical resistance
-
Low shrinkage, high dimensional accuracy
❌ Cons:
-
Slightly more challenging than PLA
-
Can be sticky on the print bed
Best for: Visual & functional prototyping, Large-format objects, End-use parts, Molds & manufacturing aids, Fit testing & concept models

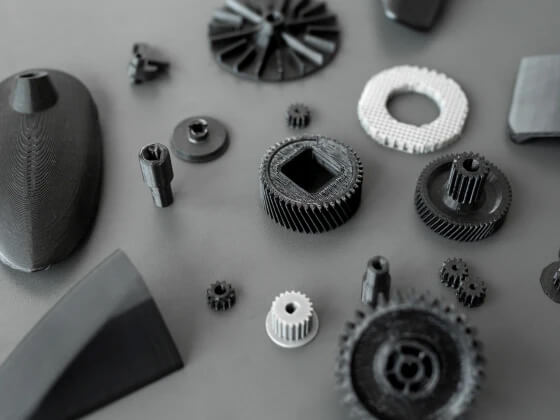
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
✅ Pros:
-
Durable and impact-resistant
-
Heat-resistant (suitable for functional parts)
-
Pre-dried for immediate use and optimal results
❌ Cons:
-
Requires a heated bed and enclosure (prone to warping)
-
Emits fumes (needs good ventilation)
Best for: Automotive: Accessory mounts, handles, hooks, Electronics: Adapters, chargers, Functional prototyping, Tooling and gears

TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)

✅ Pros:
-
Good flexibility with rubber-like texture
-
High resistance to abrasion, wear & tear
-
Chemical resistance
- Strong layer bonding
❌ Cons:
-
Difficult to print (requires slow speeds)
-
Not rigid (not suitable for structural parts)
Best for: Soft-touch multi-material models or handles, Mechanical parts, Protective covers, safety covers & bumpers, Springs, seals and shock absorbers, Wheels and rollers, Shoe soles, watch straps
Nylon
✅ Pros:
-
High strength & resistance to abrasion
-
Chemical resistance
-
Low friction coefficient & Lower warping
❌ Cons:
-
Absorbs moisture (needs dry storage)
-
Requires high printing temperatures
Best for: Functional prototypes, Making jigs and fixtures, Parts resistant to oils, fuels & chemicals, End-use parts requiring high wear resistance

2. Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Filament
A. Printability (Ease of Use)
-
Beginners: PLA is the easiest.
-
Intermediate users: PETG offers a good balance.
-
Advanced users: ABS, Nylon, and flexible filaments require more expertise.
B. Strength & Durability
-
High-strength needs? Try ABS, PETG, or Nylon.
-
Flexibility required? TPU is the best choice.
C. Temperature Resistance
-
PLA: Low (~50°C)
-
ABS & PETG: Moderate (~80-100°C)
-
Nylon & PC (Polycarbonate): High (>100°C)
D. Post-Processing & Finishing
-
Sanding & Painting: PLA and ABS work well.
-
Chemical Smoothing: ABS (acetone), PETG (limited options).
E. Safety & Ventilation
-
PLA: Safe, low odor.
-
ABS & Nylon: Require good ventilation.
3. Specialty Filaments (Beyond Standard Options)
-
WoodFill & Marble PLA & Multicolor Silk PLA : For aesthetic, textured finishes.
-
Glow-in-the-Dark & Conductive Filaments: For unique projects.
-
Carbon Fiber Reinforced: Extra strength for engineering parts.
4. Final Tips for Choosing the Best Filament
-
Start with PLA if you're new to 3D printing.
-
Need durability? PETG is a great all-rounder.
-
High-temperature applications? ABS or Nylon.
-
Flexible parts? TPU is the way to go.
-
Store filaments properly (use airtight containers with desiccants).
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D printing filament depends on your project’s needs—whether it’s strength, flexibility, heat resistance, or ease of printing. By understanding the differences between PLA, ABS, PETG, TPU, and specialty filaments, you can optimize your 3D prints for success.