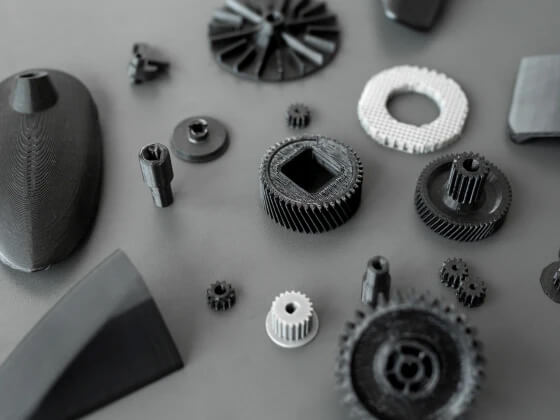
What Are Engineering Filaments?
Engineering filaments are high-performance materials designed for strength, heat resistance, chemical durability, and dimensional stability. They're used in demanding applications across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare—for prototypes, jigs, structural parts, and end-use components.
Why Use Engineering Filaments?
These filaments outperform standard materials like PLA or ABS, and can even replace traditional methods such as injection molding or CNC in some use cases.
Key Advantages:
● Mechanical Strength: Tensile strength of 50–150 MPa; high impact resistance and flexibility.
● Heat Resistance: Operate in environments from 100°C to 260°C.
● Chemical Durability: Resist oils, acids, solvents—ideal for medical and industrial parts.
● Wear Resistance: Materials like PA, PA-CF are great for gears, sliders, and moving parts.
● Functional Features:
○ Flame Retardant & Insulating (e.g. PC-ABS)
○ UV & Moisture Resistance (e.g. ASA-grade PA)
○ Lightweight (e.g. PA12-CF, PPS-CF)
○ High Transparency (e.g. PC with >90% light transmission)
Popular Engineering Filaments & Applications
|
Material |
Key Features |
Typical Applications |
|
|
lHigh toughness (impact strength: 80kJ/m²), lWear resistance (abrasion volume: 0.05mm³) lLow-temperature resistance (-40°C stable performance) lCan be reinforced with glass fiber/carbon fiber. |
Gears, bearings, moving mechanical parts, automotive seat adjusters, medical bone screw models. |
|
PC (Polycarbonate) |
lHigh strength (tensile strength: 65MPa) lHigh transparency (light transmittance: 90%) lHeat resistance (HDT 135°C) lExcellent impact resistance (Izod notched impact strength: 600J/m) |
Optical lenses, electronics housings (e.g. router cases), tool handles, car lamp covers (heat and yellowing resistance). |
|
|
lCombines PC’s strength with ABS’s ease of processing lGood toughness and surface gloss lSuitable for electroplating/spraying lBetter dimensional stability than pure ABS.
|
Industrial equipment panels, consumer electronics housings (e.g., drone bodies), decorative parts in precision instruments. |
|
|
lTop-tier heat resistance (continuous use at 260℃) lResistant to strong acids and alkalis lHigh strength (tensile strength: 100MPa) lMedically biocompatible. |
Aerospace structural parts (e.g. titanium substitutes), medical implants (e.g. spinal cages), corrosion-resistant semiconductor components. |
|
|
Carbon fiber-reinforced nylon with high strength, rigidity, impact resistance, and heat resistance. |
Automotive exhaust supports, kettle bases, pot handles, engine brackets, gears, fuel pipe connectors, wear-resistant bearings. |
|
|
Carbon fiber-reinforced PA12, featuring high strength, lightweight, low moisture absorption, heat resistance up to 175℃, and outstanding dimensional stability. |
Fuel filter housings, pipe joints, robotic arms, ski bindings, climbing buckles, customized prosthetic joints, surgical tool handles. |
|
|
Glass fiber-reinforced PA6 combining excellent mechanical performance with high strength, rigidity, and thermal resistance; excellent dimensional stability. |
Aerospace non-load-bearing components (e.g., brackets, connectors, dashboard parts), appliance housings, motor components, medical equipment shells, precision parts. |
Print Like a Pro – Tips for Engineering Filaments
1. Dry Before Use
2. PA/PC absorb moisture easily. Dry for 6–12 hours at 80–110°C before printing.Use Hardened Nozzles
3. Glass or carbon fiber-filled filaments are abrasive. Brass nozzles may clog or wear.Printer Settings
a. Nozzle Temp: 280–320°C for PC, 380–420°C for PEEK
b. Bed Temp: 60–100°C depending on material
c. Enclosure: Keeps chamber 50–70°C to prevent warping
4. Post-Processing (Annealing)
Heat parts ~10–20°C above Tg for 1–2 hours, then cool slowly. Improves strength up to 20% and reduces cracking.

Explore the Power of Industrial-Grade Materials
Engineering filaments unlock the true potential of 3D printing—from performance prototypes to functional end-use parts.
Follow @Inslogic3D for more tips, materials, and advanced 3D printing insights.